
MARS | Science
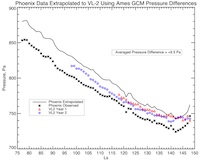
Phoenix surface pressures extrapolated to the VL-site and corrected for elevation differences and dynamics.
Full Resolution Version: 209 KB
Order high-quality reprints
Full Resolution Version: 209 KB
Order high-quality reprints
Detecting secular climate change on Mars
1Robert M. Haberle and 2Melinda A. Kahre
1Space Science and Astrobiology Division, NASA Ames Research Center, M.S. 245-3, Moffett Field, CA 94035, USA
2Bay Area Environmental Research Institute, NASA Ames Research Center, M.S. 245-3, Moffett Field, CA 94035, USA
Mars 5, 68-75, 2010 | doi:10.1555/mars.2010.0003
Received March 11, 2010 | Accepted July 23, 2010 | Published August 3, 2010
A comparison of Viking and Phoenix surface pressure data on Mars shows an increase in atmospheric mass that is consistent with that estimated to be eroding from the south polar residual cap. However, the increase does not rise above the uncertainties in the data.
PDF 2.0 MB | ZIP 3.4 MB | TAR.GZ 3.4 MB | Supporting Files